Working with Analog Write
Use PWM to control the brightness of a LED
Components Required

Introduction
Learning Outcomes
- Pulse Width Modulation
Theory
To change the brightness of a LED, we could change the voltage the LED is supplied with. But in a microcontroller, the ability to change the voltage (converting a digital number to an analog voltage) is limited, so a method called PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is used. What this does, is pulsing on and off the pin at a high frequency. The length of the pulses creates the perception of brightness.
Duty cycle is a term used to describe the ratio between on and off times.
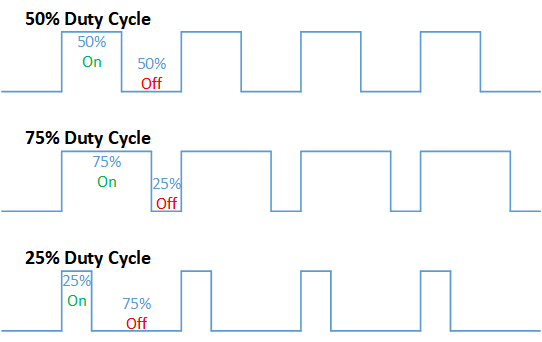
In this example, a higher Duty cycle gives higher brightness & the lower duty cycle gives lower brightness.
Methodology
Code
from machine import Pin,PWM
import time
LED=Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
pwm = PWM(LED)
pwm.freq(50)
while True:
for i in range (0,256,1):
pwm.duty(i)
time.sleep_ms(500)
Explanation
for i in range (0,256,1): There are 3 parameters in a for loop, the first parameter we are defining is the starting value for the loop. The second parameter specifies the ending value for the loop, the third parameter specifies the change that happens to the variable in each cycle, in this, i is incremented by one.
pwm.duty(i) You can input the pin number you need to do PWM and then the PWM value you need to give to that pin. This assigns the corresponding duty cycle to the pin.
Note This example we have coded to increase the brightness, write a code to do the opposite of that, to fade the brightness of the LED, & put both effects together to create a beautiful fade & light-up effect.